One thing I enjoy doing, as far as gaming (and even computing in general goes) is looking back to where we came from during my lifetime, thus far. Back in the early 90s, DOS was king and that was my introduction to the x86 world. On our 486DX-33, I explored a whole new world of computing. Around the same time, Macintoshes were big in schools and thus I had a pretty balanced upbringing in the platform world. I didn’t really get to Linux until college, but that was already–sadly–so long ago that I’m finding myself looking back similarly on that platform.
But, DOS is in the title, so we’ll look at that one. DOSBox is a popular platform for DOS emulation and will, hopefully, remain so for a long time. So, here I’d like to chronicle how I package DOS games for play on macOS. Totally a scriptable process, I think, and maybe one day I’ll get to it. But, for now, it’s a pretty manual one. I’ve been doing it this way since probably OS X Tiger, and the process hasn’t really changed much, outside of some added security features getting in the way since–for which there are valid workarounds.
Pre-requisites
- You’re going to need a local copy of DOSBox
- A DOSBox config file, tailored to your liking
- A copy of a directory containing the DOS game that you will want to be playing
First off, when I started on this little journey I had to learn a little bit about AppleScript. Specifically, functionality geared around Finder so as to determine the package’s current path so as to access the resources needed for this little package. The basic form of this AppleScript is pretty simple.
tell application "Finder"
set current_path to container of (path to me) as alias
set posix_path to POSIX path of current_path
end tell
set dosbox_path to "\"" & posix_path & "/***INSERT APP NAME HERE***.app/Contents/Resources/DOSBox\"" as string
set config_path to "\"" & posix_path & "/***INSERT APP NAME HERE***.app/Contents/Resources/dosbox.conf\"" as string
set executable_path to "\"" & posix_path & "/***INSERT APP NAME HERE***.app/Contents/Resources/***APP FOLDER***/***EXECUTABLE NAME***\"" as string
do shell script dosbox_path & " -exit -conf " & config_path & " " & executable_pathThe first lines set current path relative to where the script currently resides. The lines below this set the various paths that will be needed to run the DOS program properly–the path to the DOSBox executable, the configuration file and the DOS executable (EXE/BAT).
“APP NAME” is the name of the app in question (e.g., “Doom II”, “Quake”, “Wolfenstein 3D”, etc). “APP FOLDER” is the folder in which the game executable resides (e.g., WOLF3D, DOOM2, QUAKE, etc). And then, of course, “EXECUTABLE NAME” is the name of the executable file (with .exe or .bat extension).
The last line is the meat and potatoes of the script. Pretty simple. It just tells the instance of DOSBox within the package to run, with the configuration file given on the exe/bat file that you want to launch.
So, what we want to do is crack open Script Editor, which resides in Applications -> Utilities. Paste this code into a new script window, substituting the app, folder and executable names (delimited by *** … ***). Save this script. When you go to save, you’ll find a dialog that looks like this
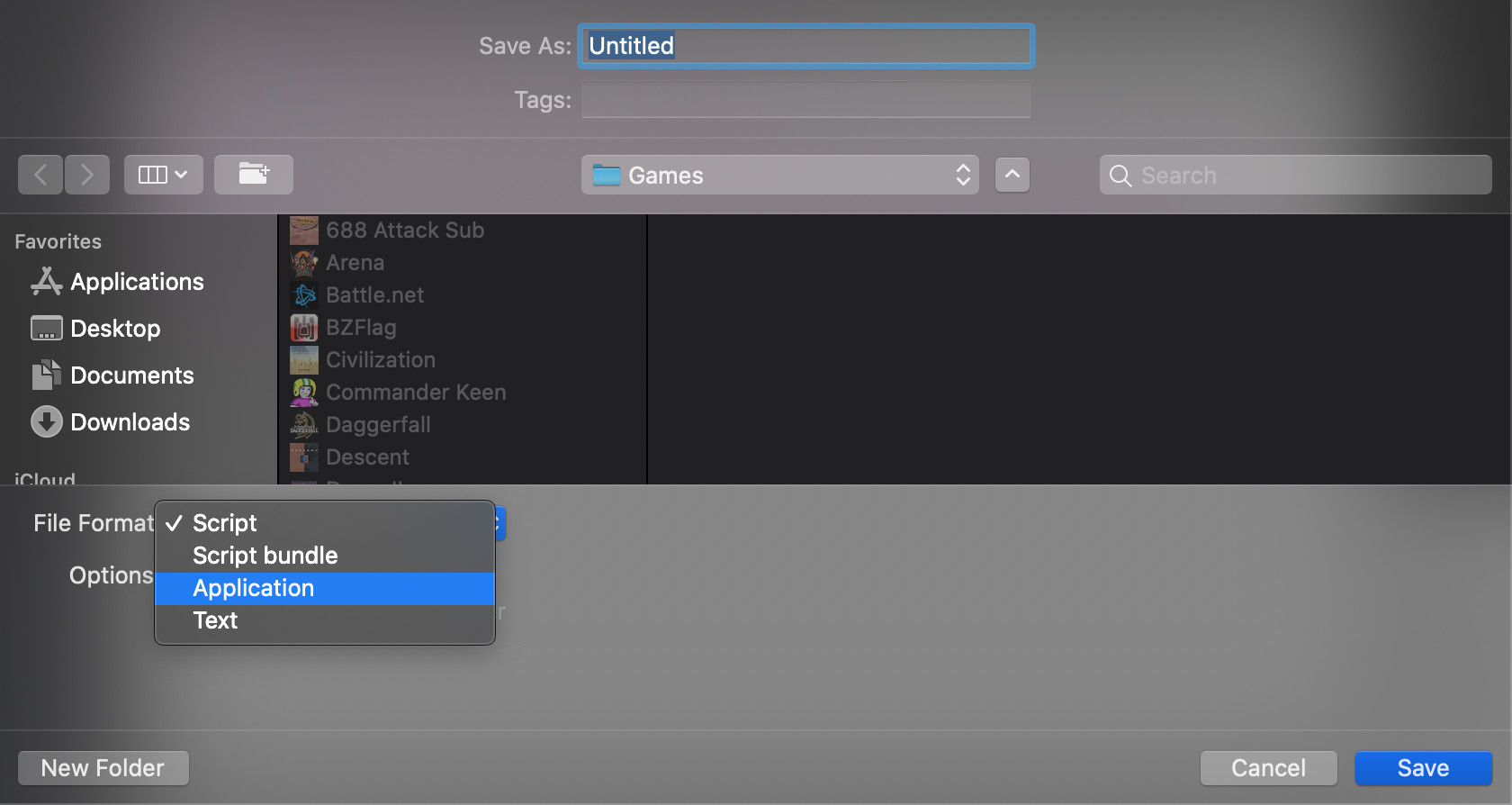
The key here is to use “Application” as the file format, and also to save as the “APP NAME” you define above in the script.
Once this is done, Right-click on the file wherever you may have saved it and click “Show Package Contents”. In Finder, you’ll see a “Contents” folder. Click into that and you’ll see a few more folders/files. The one we’re concerned with here is “Resources”. Click into that folder and you’ll see a few files and folders–including a “Scripts” folder which contains the script that you just saved. We don’t really have to worry about that any more, at this point, though.
What you want to next is copy over your DOS directory over into this Resources folder.
After this, you’re going to want to snag a copy of the DOSBox executable from its package (default install folder for that is in “Applications”). Right-click on that app, and again select “Show Package Contents”. Go into Contents->MacOS, select the DOSBox file that’s in that folder, copy it, and paste it into the Resources folder of your new shiny app that you made. We’re doing this step so as to make your package self-contained, so that it doesn’t have to necessarily rely on DOSBox being installed on your machine (e.g., if you throw it on another machine). It’s a relatively small executable (11MB), so it doesn’t generally bother me to have multiple copies of it–though, you could probably use soft links to achieve the same goals without multiplying the number of executables.
So, now that we have that out of the way, we need to copy over our DOSBox config file into that Resources directory.
In the end, you should have your DOS folder containing the game resources and executables, the DOSBox executable, and DOSBox config file all in that same Resource folder.
At this point, your package should be runnable. One thing I like to do to cap it off is to add an icon, so that it doesn’t have that funny default script icon. To do this, you’ll need an icon file (.icns). You can find an image you want to use on the vast Internet, and convert it to .icns. There are a number of online converters out there or, if you really don’t trust them, you could always use your image editor of choice and/or the SIPS utility from the Terminal.
Once you have an ICNS file, no matter how you slice it, all you have to do is right-click on your app and select “Get Info”. Take your ICNS file and drag it up into the image area of this dialog and that will give your app the icon you’ve always wanted. Since there weren’t really icons back in DOS days, it’ll never be completely authentic. Personally, I just generally find images which can be recognizable as being associated with the game in question and can be seen at that kind of a scale and just roll with it.
The last thing we need to look at is the fact that this script is going to access Finder.
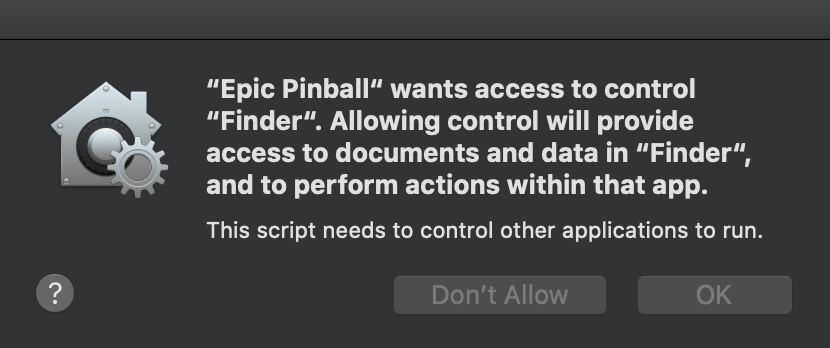
You can click OK to continue, but you’ll get this dialog every other time you run your program if you don’t allow access. To do this, once you’ve first launched the program, exit out of it and you should see a dialog that looks a little something like this:
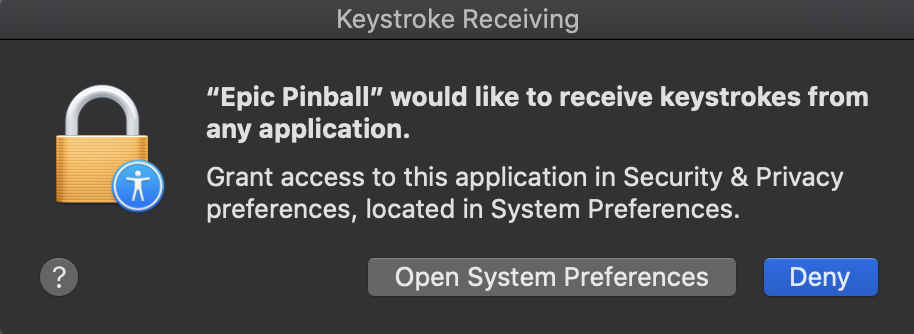
Click “Open System Preferences”, and you’ll be in the “Security & Privacy” section. Make sure that the program you want to run has a checkbox next to it (after unlocking the pane with your password or fingerprint, whichever may apply).
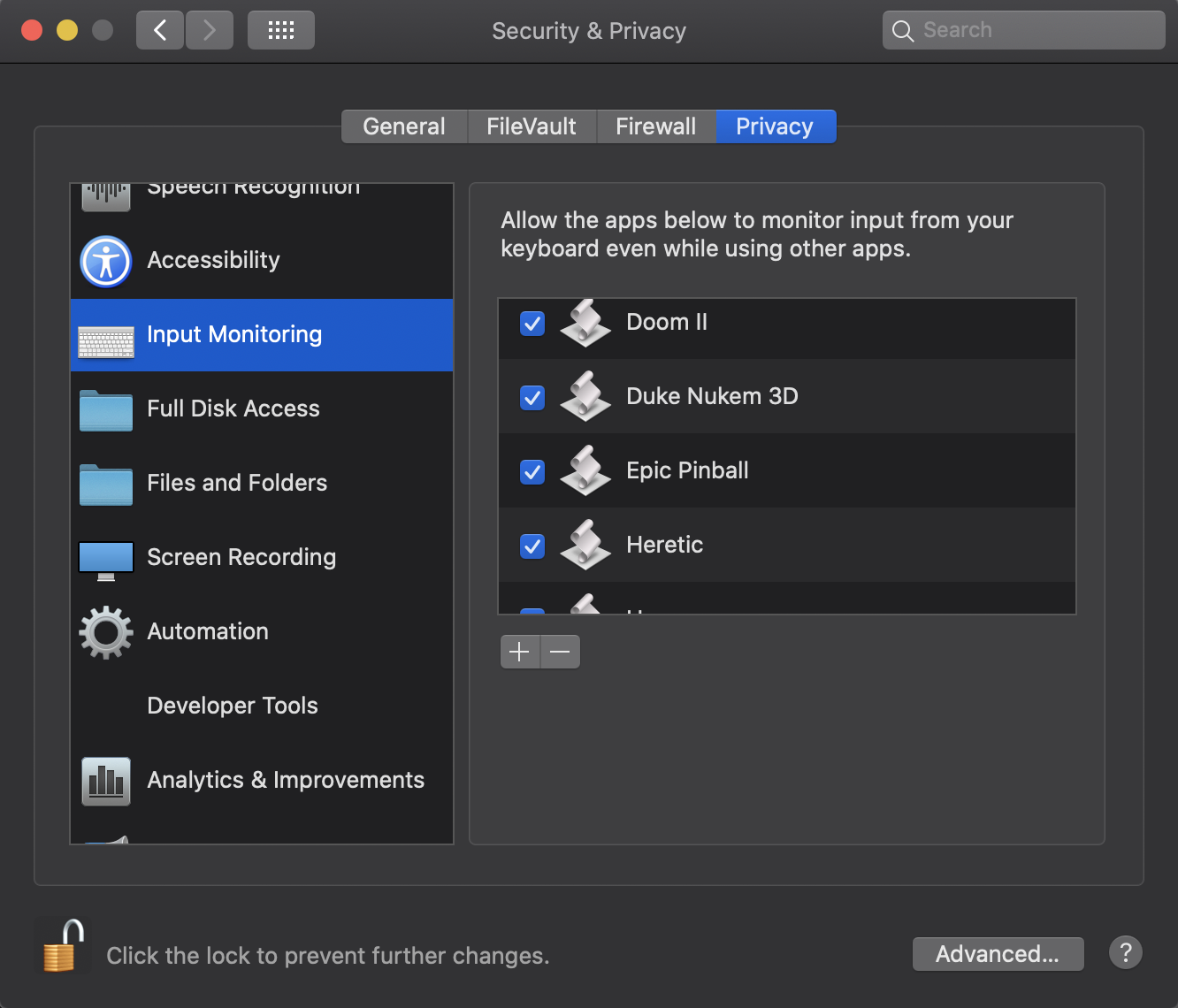
And, voila! You shouldn’t be pestered with this particular dialog again–unless Apple starts clamping down further. I really can’t blame them. We’re doing script kiddie things here, and macOS has no idea who we are–as an enthusiast, I don’t necessarily see the need to digitally sign this kind of stuff…so, I won’t for as long as I can avoid it 😉
So, that’s about it. That’s a method of setting up nice, neat little app packages for all of your old DOS games that you thought you’d never see again. Obviously, you can really do this for any DOS program, not just games, but I don’t exactly find much utility in Word for DOS anymore 😉 But, if you’re the nostalgic type who has some favorite DOS program out there, this process should work just fine for those.
Alas, at this point, it’s not nearly so neat and tidy a process for Windows or Linux–just simple shortcuts for those, with a dependency on a DOSBox installation somewhere on the machine. Ultimately, the same effect, though.